A ball of mass 0.15 kg is dropped from a height. 10 m, strikes the ground and rehounds to the same height. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the ball is (g = 10 m/s² ) nearly:
A ball of mass 0.15 kg is dropped from a height. 10 m, strikes the ground and rehounds to the same height. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the ball is (g = 10 m/s² ) nearly:
Velocity just before striking the ground
v? = √2gh
v? = √ (2*10*10) = 10√2 m/s
v? = -10√2?
If it reaches the same height, speed remains same after collision only the direction changes.
v? = 10√2 m/s
v? = 10√2?
|Impulse| = m|Δv|
= m|10√2? - (-10√2? )|
= 0.15 [2 (10√2)]
= 3√2 kg m/s
= 4.2 kg m/s
Similar Questions for you
From A to B the process is isobaric
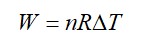
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Work, Energy and Power 2021
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering