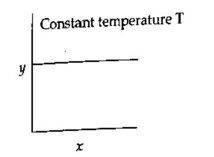
The given graph is a representation of kinetics of a reaction.
The y and x axes respectively are for zero and first order reactions, respectively are:
The given graph is a representation of kinetics of a reaction.
The y and x axes respectively are for zero and first order reactions, respectively are:
For a zero-order reaction Rate Vs conc graph will be straight line parallel to the x-axis.
For a 1st order reaction t? /? vs concentration will again be a straight line parallel to x-axis.
Similar Questions for you
ΔG° = –RT * 2.303 log K
–nFE° = +RT * 2.303 log K
2 * 96500 * 0.295 = 8.314 * 298 * 2.303 log10 K
10 = log10 K = 1010
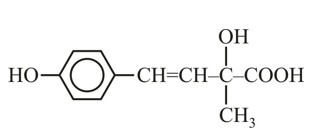
It has chiral centre and differently di substituted double bonded carbon atoms.
Rate of ESR ∝ No. of α – H (Hyperconjugation)
Cr3+ion is a most stable in aqueous solution due to. t2g half filled configuration
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Chemical Kinetics 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering