3.31 Three electrolytic cells A, B, C containing solutions of ZnSO4 , AgNO3 and CuSO4 , respectively are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5 amperes was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and zinc were deposited?
3.31 Three electrolytic cells A, B, C containing solutions of ZnSO4 , AgNO3 and CuSO4 , respectively are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5 amperes was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and zinc were deposited?
Equivalent weight is Ag, EAg = 180/1 = 180
Equivalent weight is Cu, ECu = 63.5 / 2 = 31.75
Equivalent weight is Zn, EZn= 65/2 = 32.5
Using Faraday's second law of electrolysis, to find the mass of Cu and Zn, we use Equation 1,
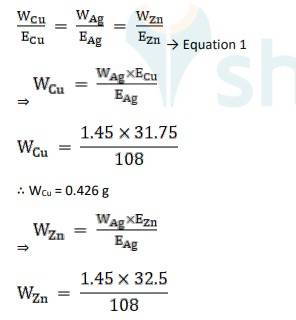
∴ WZn = 0.436 g
To find the time of current flow, using Faraday's first law
Similar Questions for you
n = 3
t = 3 * 1580
= 4740 years
The following are the real-world applications of electrochemistry - military applications such as thermal batteries, digital watches, hearing aids, digital cameras, electrical appliances such as cellphones, and torches.
It depends on students. Though it is not a tough chapter to study but for students who have misconceptions and those who struggle with visualization can find it challenging.
There are two types of electrochemical cells - Electrolytic and Galvanic or Voltaic cells. The electrolytic cells need an external source such as AC power source or DC battery and it involve non-spontaneous reactions. The galvanic cells gets its energy from redox reactions which is spontaneous.
Redox reactions is the basic principle of the electrochemistry. The redox reactions is the process where electrons are transferred between substances. In this process chemical energy gets converted into electrical energy and vice versa.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
