4.29 For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K, the following data are obtained.
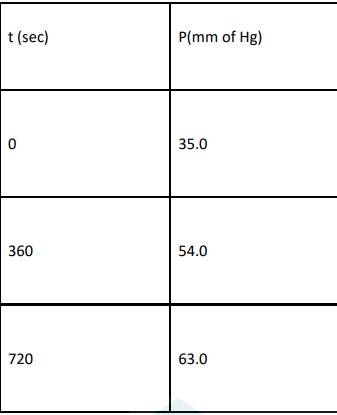
Calculate the rate constant.
4.29 For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K, the following data are obtained.

Calculate the rate constant.
4.29 When t = 0, the total partial pressure is P0 = 35.0 mm of Hg
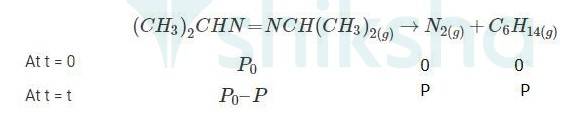
When time t = t, the total partial pressure is Pt = P0 + p
P0-p = Pt-2p, but by the above equation, we know p = Pt-P0 Hence, P0-p = Pt-2 ( Pt-P0)
Thus, P0-p = 2P0 – Pt
We know that time
t= 2.303/K log R0 / R
Where, k- rate constant
[R]° -In
Similar Questions for you
Kindly go through the solution
Ea = 216.164kJ/mol 216
Reaction rate is used to measure how fast or slow reactions occur per unit time. The rate constant is a proportionality factor that remains constant for every reaction.
Yes, in elementary reactions, order and molecularity can be the same, but this is not always the case because order is an experimental quantity, and molecularity is a theoretical concept.
Reaction Kinetics, also known as chemical kinetics, is the study of the rate of chemical reaction and the factors affecting the reaction rate, such as temperature, concentration, and catalyst.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
