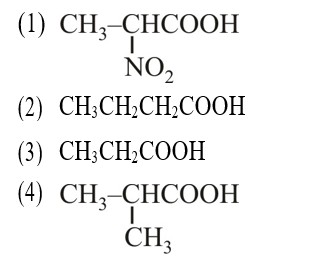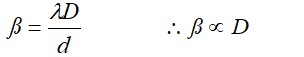Match the pollutant(s) in Column I with the effect(s) in Column II.
Column I
Column II
(i) Oxides of sulphur
(a) Global warming
(ii) Nitrogen dioxide
(b) Damage to kidney
(iii) Carbon dioxide
(c) 'Blue baby' syndrome
(iv) Nitrate in drinking water
(d) Respiratory diseases
(v) Lead
(e) Red haze in traffic and congested areas.
Match the pollutant(s) in Column I with the effect(s) in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Oxides of sulphur |
(a) Global warming |
|
(ii) Nitrogen dioxide |
(b) Damage to kidney |
|
(iii) Carbon dioxide |
(c) 'Blue baby' syndrome |
|
(iv) Nitrate in drinking water |
(d) Respiratory diseases |
|
(v) Lead |
(e) Red haze in traffic and congested areas. |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)→ (d); (ii)→ (e); (iii)→ (a); (iv)→ (c) ; (v)→ (b)
Similar Questions for you
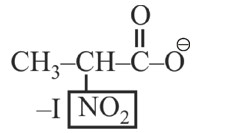
–I effect ∝ Acidic strength
+I effect ∝ Basic strength
* Most stable anion due to maximum –I effect.
* Most acidic
with increase in separation of screen from slits plane, fringe width increases.
Excessive nitrate in drinking water causes methemoglobinemia
Excessive nitrate in drinking water causes methemoglobinemia
Release of toxic/undesirable materials in the environment.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Fourteen 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering