The secondary structure of protein is stabilised by:
The secondary structure of protein is stabilised by:
In proteins, the secondary structure (such as α-helices and β-sheets) is stabilized by hydrogen bonds formed between the carbonyl oxygen of one peptide bond and the amide hydrogen of another.
Similar Questions for you
Insulin is a globular proteins.
Primary structure of protein in unaffected by physical or chemical changes.
For stabilization of a - helix structure of protein, H-bonding is responsible which is in between 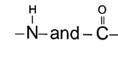
CH? (methane) is produced / generated from paddy fields. And methane leads to both global warming and photochemical smog.
CO? is used in photosynthesis, acid rain etc. but methane is not consumed.
So methane is a stronger global warming gas than CO?
Linear: N? (azide ion)
Bent-shape: O? (ozone), NO? (nitrite ion), Cl? O (dichlorine monoxide)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering

