Let P be the plane containing the straight line and perpendicular to the plane containing the straight lines If d is the distance of P from the point (2, -5, 11), then d2 is equal to:
Let P be the plane containing the straight line and perpendicular to the plane containing the straight lines If d is the distance of P from the point (2, -5, 11), then d2 is equal to:
Let a, b, c be direction ratios of plane containing lines
and
Equation of plane P is : 1 (x – 3) 1 (y + 4) + 2 (z – 7) = 0
Distance from point (2, 5, 11) is
Similar Questions for you
....(1)
Let
Let
Put l1 and l2 in (1)
α = 3
Given , ,
Dot product with on both sides
... (1)
Dot product with on both sides
... (2)
(a – 1) × 2 + (b – 2) × 5 + (g – 3) × 1 = 0
2a + 5b + g – 15 = 0
Also, P lie on line
a + 1 = 2λ
b – 2 = 5λ
g – 4 = λ
2 (2λ – 1) + 5 (5λ + 2) + λ + 4 – 15 = 0
4λ + 25λ + λ – 2 + 10 + 4 – 15 = 0
30λ – 3 = 0
a + b + g = (2λ – 1) + (5λ + 2) + (λ + 4)
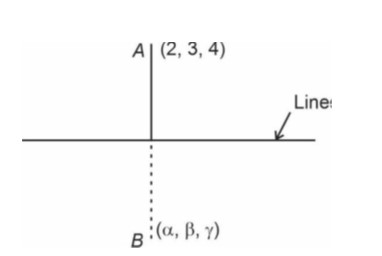
Take
x = 2λ + 1, y = 3λ + 2, z = 4λ + 3
= (α − 2)
Now,
(α − 2) ⋅ 2 + (β − 3) ⋅3 + (γ − 4) ⋅ 4 = 0
2α − 4 + 3β − 9 + 4γ −16 = 0
⇒ 2α + 3β + 4γ = 29
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eight 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
