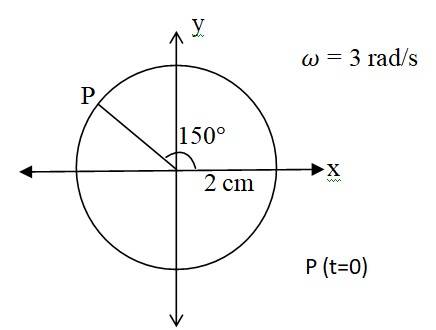
14.12 Plot the corresponding reference circle for each of the following simple harmonic motions. Indicate the initial (t =0) position of the particle, the radius of the circle, and the angular speed of the rotating particle. For simplicity, the sense of rotation may be fixed to be anticlockwise in every case: (x is in cm and t is in s).
(a) X = –2 sin (3t + /3)
(b) X = cos ( 6 – t)
(c) X = 3 sin (2 t + /4)
(d) X = 2 cos t
14.12 Plot the corresponding reference circle for each of the following simple harmonic motions. Indicate the initial (t =0) position of the particle, the radius of the circle, and the angular speed of the rotating particle. For simplicity, the sense of rotation may be fixed to be anticlockwise in every case: (x is in cm and t is in s).
(a) X = –2 sin (3t + /3)
(b) X = cos ( 6 – t)
(c) X = 3 sin (2 t + /4)
(d) X = 2 cos t
(a) X = -2 sin( 3t + ) = +2cos ( 3t + + = 2 cos (3t + )
when we compare this equation with standard SHM equation
x = Acos ( t + ), then we get
Amplitude A = 2 cm. Phase angle = 150 , angular velocity = 3 rad/s
(b) X= cos ( t) = cos ( )
when we compare this equation with standard SHM equation
x
Similar Questions for you
Velocity of block in equilibrium, in first case,
Velocity of block in equilibrium, is second case,
From conservation of momentum,
Mv = (M + m) v’
f? = 300 Hz
3rd overtone = 7f? = 2100 Hz
Kindly consider the following figure
K = U
½ mω² (A² - x²) = ½ mω²x²
A² - x² = x²
A² = 2x²
x = ± A/√2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

physics ncert solutions class 11th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering