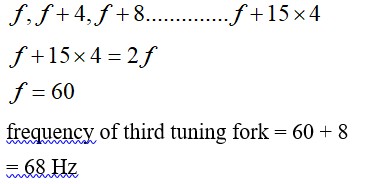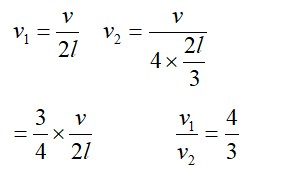15.26 Earthquakes generate sound waves inside the earth. Unlike a gas, the earth can experience both transverse (S) and longitudinal (P) sound waves. Typically the speed of S wave is about 4.0 km s–1, and that of P wave is 8.0 km s–1. A seismograph records P and S waves from an earthquake. The first P wave arrives 4 min before the first S wave. Assuming the waves travel in straight line, at what distance does the earthquake occur ?
15.26 Earthquakes generate sound waves inside the earth. Unlike a gas, the earth can experience both transverse (S) and longitudinal (P) sound waves. Typically the speed of S wave is about 4.0 km s–1, and that of P wave is 8.0 km s–1. A seismograph records P and S waves from an earthquake. The first P wave arrives 4 min before the first S wave. Assuming the waves travel in straight line, at what distance does the earthquake occur ?
Let and be the velocities and and be the time taken to reach the seismograph from the epicentre of S and P waves respectively.
Let L be the distance between the epicentre and the seismograph.
We have:
L = …. (i)
L = …. (ii)
It is given, = 4 km/s and = 8 km/s
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
4 =
Similar Questions for you
The acceleration of wave is g/2. Its speed increases as it moves up. So answer is (2)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering