A block of mass 1 kg attached to a spring is made to oscillate with initial amplitude of 12cm. After 2 minutes the amplitude decreases to 6cm. Determine the value of the damping constant for this motion. (take ln 2 = 0.693)
A block of mass 1 kg attached to a spring is made to oscillate with initial amplitude of 12cm. After 2 minutes the amplitude decreases to 6cm. Determine the value of the damping constant for this motion. (take ln 2 = 0.693)
Option 1 - <p>3.3 × 10⁻² kg s⁻¹</p>
Option 2 - <p>1.16 × 10⁻² kg s⁻¹<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 3 - <p>0.69 × 10⁻² kg s⁻¹</p>
Option 4 - <p>5.7 × 10⁻³ kg s⁻¹</p>
2 Views|Posted 5 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
A
Answered by
5 months ago
Correct Option - 4
Detailed Solution:
Given the decay equation A = A? e^ (-bt/m):
-bt/m = ln (A/A? )
Solving for b:
b = (-m/t? ) * ln (A/A? ) = (-1 / (2 * 60) * ln (6/12) = 5.775 * 10? ³ kg/s
Similar Questions for you
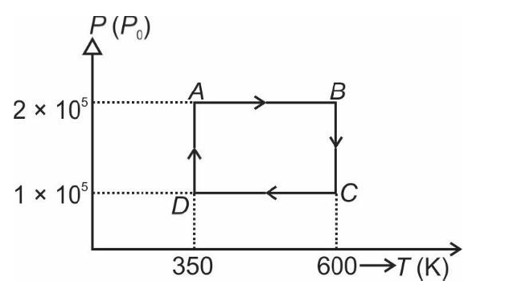
From A to B the process is isobaric
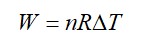
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Physics Oscillations 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering