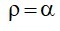A spherically symmetric charge distribution is considered with charge density varying
![]()
as
Where, r(r < R) is the distance from the centre O (as shown in figure). The electric field at point P will be:
A spherically symmetric charge distribution is considered with charge density varying
as
Where, r(r < R) is the distance from the centre O (as shown in figure). The electric field at point P will be:
As,
Similar Questions for you
The following are the topics covered in this chapter: Electric Field and Field Lines, Gauss's Law, Electric Dipole, Conductors and Insulators, and Electric Flux.
Indeed, it is an easy chapter of Class 12 Physics. In this chapter, you will learn about the foundational concepts like Gauss's law and electric fields.
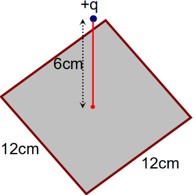
Flux through the 6 sides of square (i.e. cube)
Flux through a square
In the medical entrance test NEET, this chapter has a moderate weightage. You can expect around 2-3 questions of this chapter that contributes to the 3-5% of the total marks in the Physics section.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering