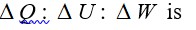For an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas, the fractional change in its pressure is equal to ( where γ is the ratio of specific heats):
For an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas, the fractional change in its pressure is equal to ( where γ is the ratio of specific heats):
Option 1 - <p>-γ(dV/V)<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 2 - <p>dV/V<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 3 - <p>-γ(V/dV)</p>
Option 4 - <p>-(1/γ)(dV/V)</p>
3 Views|Posted 5 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
V
Answered by
5 months ago
Correct Option - 1
Detailed Solution:
PV? = C ⇒ V? (dP/dV) + P (γV^ (γ-1) = 0 ⇒ dP/dV = -γ (P/V) ⇒ dP/P = -γ (dV/V)
Similar Questions for you
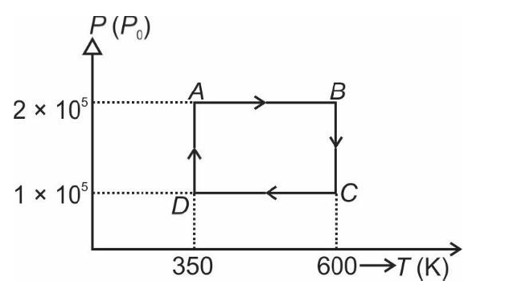
From A to B the process is isobaric
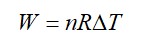
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Heat is path dependent so path function but internal energy does not depend on path chosen.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering