(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as w(b) =w0– b2/α , where b is the vertical distance from the pole, w0is a constant. Using Fermat's principle, i.e., the time of transit fora ray between the source and observer is an extremum find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
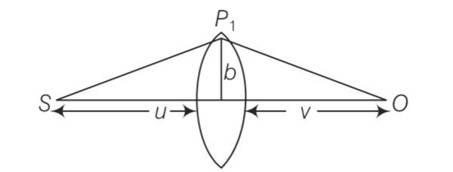
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as w(b) =w0– b2/α , where b is the vertical distance from the pole, w0is a constant. Using Fermat's principle, i.e., the time of transit fora ray between the source and observer is an extremum find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Time from S to P1 is
t1 =
Time from P1 to O is
t2 = ;
the time required travel through lens is t1 =
so total time is t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)(wo+b2/ ))
after solving we get
differentiating with respect to time
t=1/c(u+v+b2/2D+(n-1)K1In(K2
Similar Questions for you
A total refractive prism is also known as a total internal reflection prism. It is an optical prism that is designed for reflecting 100% of the incident light. This happens since this prism uses the principle of total internal reflection. These prisms are oriented and shaped in a specific way so tha
Total deviation in a prism is the total angle by which the light ray gets bent as it passes through the prism. It is an angle between incident ray and emergent ray of the prism. When a light enters the prism, it will bend towards the normal. After that, it will travel through the prism and bend away
There are different types of glasses that are used in optical instruments, including the following:
Crown glass (K): This glass is used in eyeglasses, microscopes and cameras. It is used in prisms and windows in optical systems. Crown glass has a low refractive index, low dispersion and excellent tra
Optical instruments can have some of the following defects that may impact their performance, which have arisen due to design limitations, manufacturing and physical properties of light:
- Chromatic Aberration: This defect occurs because of the different wavelengths of light that refract at slightly di
Yes, optical instruments are used in modern medicine for many purposes including surgery, monitoring, research and diagnosis. Let us take a look at each one by one:
- Many optical instruments are used for visualizing internal structures for diagnosis of a disease and its monitoring. These include Ophth
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
