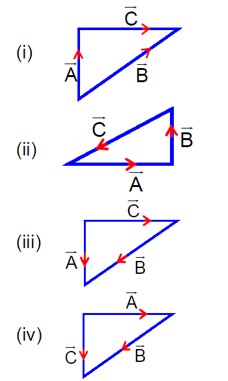
Match List I with List II.
List - I
List - II
(a) C - A - B = 0
(i) Diagram showing A + B = C
(b) A - C - B = 0
(ii) Diagram showing C + B = A
(c) B - A - C = 0
(iii) Diagram showing A + C = B
(d) A + B = -C
(iv) Diagram showing A + B + C = 0
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List I with List II.
|
List - I |
List - II |
|
(a) C - A - B = 0 |
(i) Diagram showing A + B = C |
|
(b) A - C - B = 0 |
(ii) Diagram showing C + B = A |
|
(c) B - A - C = 0 |
(iii) Diagram showing A + C = B |
|
(d) A + B = -C |
(iv) Diagram showing A + B + C = 0 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
From triangle law of addition, we can clearly write answer.
Similar Questions for you
Polygon law is applicable in both the situation given but the equation given in the reason is not useful in explaining the assertion.
let the angle between is , so according to question, we can write
Graphically, we place vectors head-to-tail. Analytically, we add components along axes using coordinate geometry, trigonometric functions, and unit vectors for precise vector resultant calculation.
It resolves vectors into components, adds corresponding x and y values algebraically, then reconstructs the resultant using magnitude and direction. That is, applying vector addition rules.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Motion in Plane 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering