The instantaneous velocity of a particle moving in a straight line is given as v = αt + βt², where α and β are constants. The distance travelled by the particle between 1s and 2s is :
The instantaneous velocity of a particle moving in a straight line is given as v = αt + βt², where α and β are constants. The distance travelled by the particle between 1s and 2s is :
Option 1 - <p>α/2 + β/3</p>
Option 2 - <p>3α/2 + 7β/3<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 3 - <p>3α/2 + 7β/2<br><!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><br><!--[endif]--></p>
Option 4 - <p>3α + 7β</p>
2 Views|Posted 5 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
A
Answered by
5 months ago
Correct Option - 2
Detailed Solution:
v =? t +? t²
ds/dt =? t +? t²
? this =? (? t +? t²)dt from 1 to 2
s = [? t²/2 +? t³/3] from 1 to 2
s = [? (2)²/2 +? (2)³/3] - [? (1)²/2 +? (1)³/3]
s = [2? + 8? /3] - [? /2 +? /3]
s = 3? /2 + 7? /3
Similar Questions for you
From A to B the process is isobaric
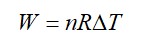
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Physics Motion in Straight Line 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering