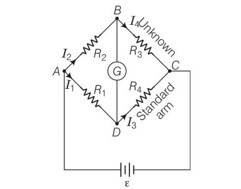
The measurement of an unknown resistance R is to be carried out using Wheatstone bridge as given in the figure. Two students perform an experiment in two ways. The first student takes R2= 10 Ω and R1 = 5 Ω. The other student takes R2 = 1000 Ω, and R1 = 500 Ω. In the standard arm, both take R3 = 5 Ω.
Both find R = R2/R1, R3 = 100 Ω within errors.
(a) The errors of measurement of the two students are the same
(b) Errors of measurement do depend on the accuracy with which R2 and R1 can be measured
(c) If the student uses large values of R2 and R1, the currents through the arms will be feeble. This will make determination of null point accurately more difficult.
(d) Wheatstone bridge is a very accurate instrument and has no errors of measurementAnswer – (b,c)
The measurement of an unknown resistance R is to be carried out using Wheatstone bridge as given in the figure. Two students perform an experiment in two ways. The first student takes R2= 10 Ω and R1 = 5 Ω. The other student takes R2 = 1000 Ω, and R1 = 500 Ω. In the standard arm, both take R3 = 5 Ω.
Both find R = R2/R1, R3 = 100 Ω within errors.
(a) The errors of measurement of the two students are the same
(b) Errors of measurement do depend on the accuracy with which R2 and R1 can be measured
(c) If the student uses large values of R2 and R1, the currents through the arms will be feeble. This will make determination of null point accurately more difficult.
(d) Wheatstone bridge is a very accurate instrument and has no errors of measurementAnswer – (b,c)
Answer – (b, c)
Explanation – According to the relation that p/q=r/s if galvanometer shows no deflection. In the above equation the value of R4 depends upon R1 and R2 . if the value of R1 and R2 will be feeble the value of R4 would be affected.
Similar Questions for you
According to this chapter, a galvanometer is used to find and measure the small electric currents in a circuit. The principle that works in a galvanometer is the electromagnetic induction.
There are two types of electricity - Static and Current electricity. The electric charges buildup on a material's surface is called the static electricity. The continuous flow of electric charge is termed as the current electricity. Current electricity is of two types - Alternating Current (AC) and
The current's SI unit is ampere. The symbol for ampere is A. The term ampere is named after the French physicist André-Marie Ampère.
In simple words, current electricity can be defined as the electric charge continuously moving from one place to another along a pathway. It is measured in amperes (A). Electric current is needed for electrical devices to work.
No, in fact, it is one of the easiest chapter of class 12 Physics. Other chapters which are considered comparatively easy are Ray Optics and Electric Charges and Fields.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
