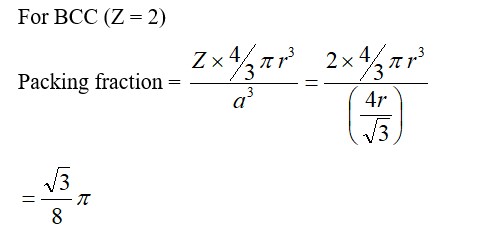1.30 'Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting points'. Comment. Collect melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane from a data book. What can you say about the intermolecular forces between these molecules?
1.30 'Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting points'. Comment. Collect melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane from a data book. What can you say about the intermolecular forces between these molecules?
1.30 Stability of a crystal is directly proportional to the magnitude of its melting points. Higher is the magnitude of forces holding the constituent particles together, higher will be the melting point and higher will be the stability. Thus ionic crystals (NaCl, KNO3 etc.) have very high melting p
Similar Questions for you
ΔG° = –RT * 2.303 log K
–nFE° = +RT * 2.303 log K
2 * 96500 * 0.295 = 8.314 * 298 * 2.303 log10 K
10 = log10 K = 1010
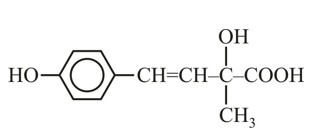
It has chiral centre and differently di substituted double bonded carbon atoms.
For FCC lattice
Packing efficiency = 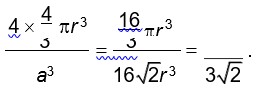
CsCl has BCC structure in which Cl– is present at corners of cube and Cs+ at body centre
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering