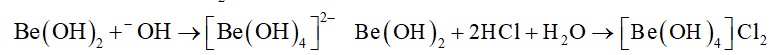10.24. Explain the significance of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium in biological fluids.
10.24. Explain the significance of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium in biological fluids.
0 Views|Posted 9 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
V
Answered by
9 months ago
Sodium:
- Na+ions participate in the transmission of nerve signals, in regulating the flow of water across cell membranes.
- In the transport of sugars and amino acids into cell.
Potassium:
- K+ions activate many enzymes.
- Participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP.
Magnesium:
- All enzymes that utilise
Similar Questions for you
Li+ has the highest hydration enthalpy.
Hence it is most hydrated
Therefore, Correct order of hydrated radii is Cs+ < Rb+ < K+ < Na+ < Li+
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering