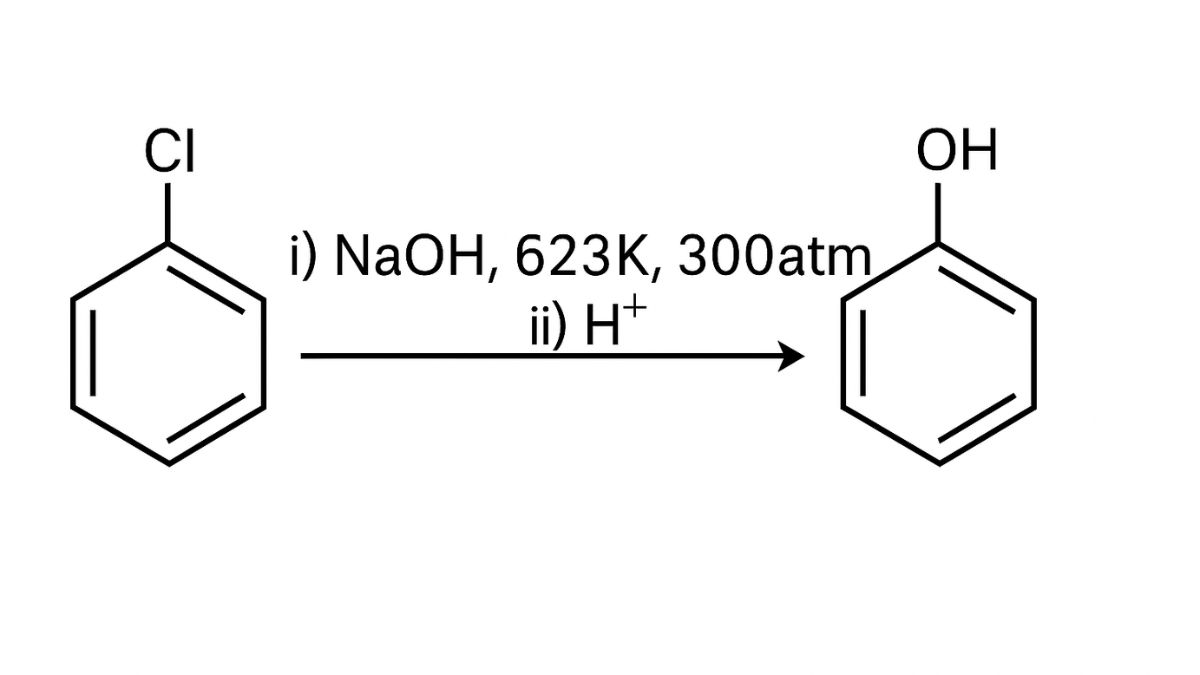
10.32 What happens when (i) N-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH (ii) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether (iii) Chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis (iv) Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH (v) Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether (vi) Methyl chloride is treated with KCN?
10.32 What happens when (i) N-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH (ii) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether (iii) Chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis (iv) Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH (v) Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether (vi) Methyl chloride is treated with KCN?
-
1 Answer
-
This is a classic question from the chapter Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. Let us solve each one as follows:
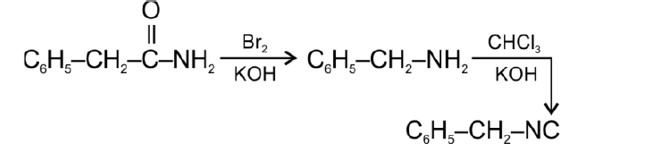
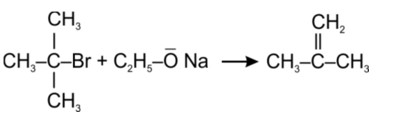
(1) When n - butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH, the formation of but - l - ene takes place. This reaction is a dehydrohalogenation reaction.
When N-butyl chloride or 1-chlorobutane is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH), elimination reaction takes place. This leads to alkene formation. 1-butene is the major product here.
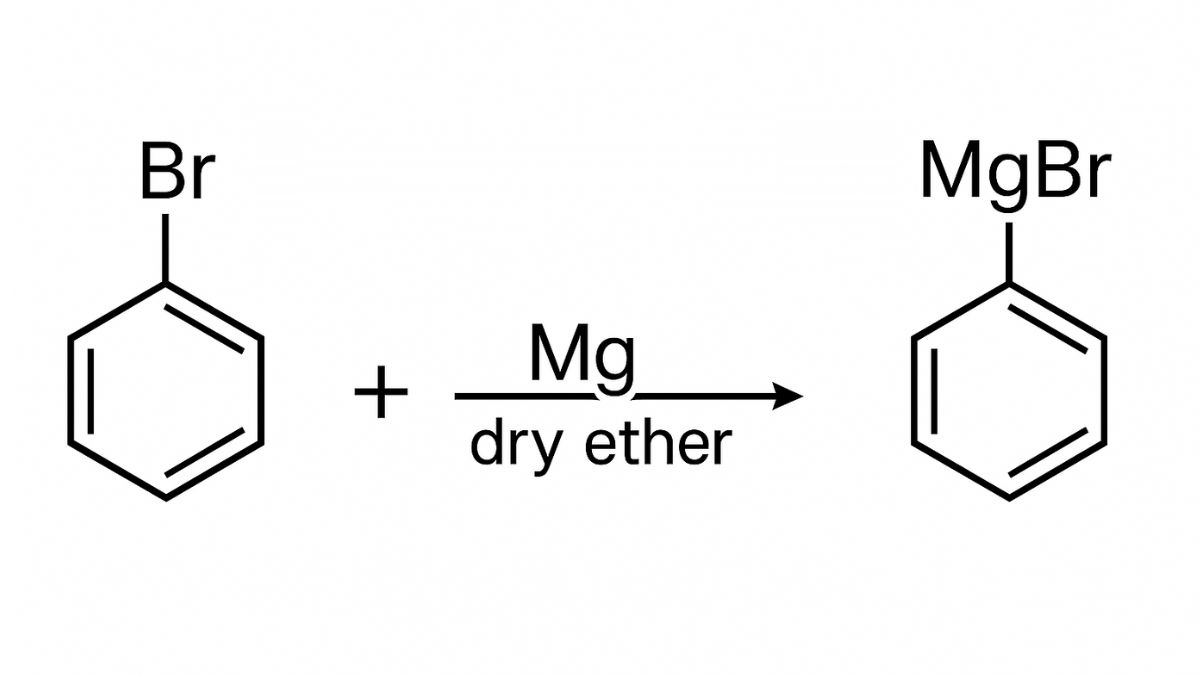
(ii) When Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether, it undergoes a reaction to produce phenylmagnesium bromide which is the Grignard reagent. This reagent is very re
...more
Similar Questions for you
Photodiode in reverse bias mode is used as intensity measuring device.
Tertiary haloalkane does not undergo SN2 reaction
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers