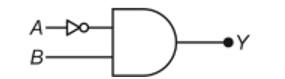
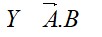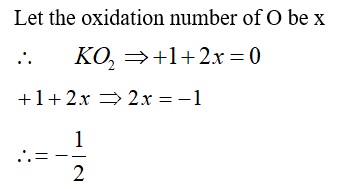11.20. What happens when
(a) Borax is heated strongly,
(b) Boric acid is added to water,
(c) Aluminium is treated with dilute NaOH,
(d) BF3 is reacted with ammonia?
11.20. What happens when
(a) Borax is heated strongly,
(b) Boric acid is added to water,
(c) Aluminium is treated with dilute NaOH,
(d) BF3 is reacted with ammonia?
(a) When borax is heated strongly, it loses water and swells into the white mass, which on further heating melts to form a transparent glassy solid called borax glass and borax bead.
Na2B4O710H2O→ Na2B4O7+ 10H2O
Na2B4O7 → 2NaBO2+ B2O3
(b) When boric acid is added to water, it accepts electrons from
Similar Questions for you
From BF3 to BI3 Lewis acidic strength increases
F2 is the strongest oxidising agent
HClO4 is the most acidic compound.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering