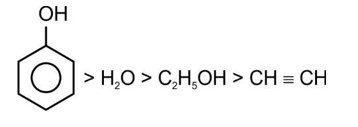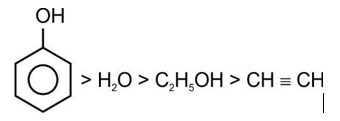11.71 Explain the following with an example. (i) Kolbe's reaction. (ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction. (iii) Williamson ether synthesis. (iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
11.71 Explain the following with an example. (i) Kolbe's reaction. (ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction. (iii) Williamson ether synthesis. (iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
11.71
Kolbe's Reaction: it is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide (the sodium salt of phenol)with carbon dioxide under pressure (100 atm,125°C), then treating the product with a sulphuric acid. The final product is salicylic acid (the precursor to aspirin).
The
Similar Questions for you
Rainbow is formed due to internal reflection and dispersion.
Correct order of acidic strength
Correct order of acidic strength
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering