14.17 What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? (i) HI (ii) Bromine water (iii) HNO3
14.17 What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? (i) HI (ii) Bromine water (iii) HNO3
14.17
When D-glucose is heated and treated with HI for a long period of time, then n-hexane is formed, which shows that all the six-carbon atoms are linked in a straight
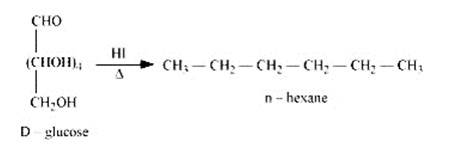
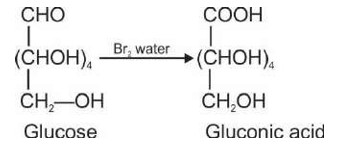
2. When D-glucose is treated with Br2 water i.e., bromine water which is a mild oxidising agent, then we get D-gluconic acid as one
Similar Questions for you
Insulin is a globular proteins.
Ionisation enthalpy increases in a period. Z dominates over screening effect (s) in a period as Zeff. increases.
Kindly go through the solution
Histidine is an essential amino acid
Lactose is a disaccharide which is formed by forming C? -C? glycosidic linkage between D-galactose and D- glucose.
Lactose - (Hydrolysis)-> D - galactose + D - glucose
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering