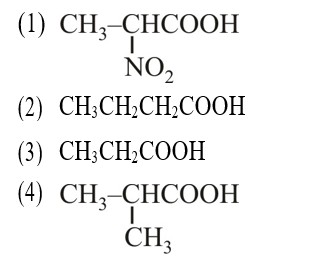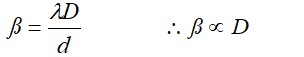14.40. Define (a) eutrophication (b) pneumoconiosis (c) Photochemical smog (d) Classical smog
14.40. Define (a) eutrophication (b) pneumoconiosis (c) Photochemical smog (d) Classical smog
(a) Eutrophication: When the growth of algae increases in the surface of water, dissolved oxygen in water is reduced. This phenomenon is known as eutrophication. (Due to this growth of fish gets inhibited).
(b) Pneumoconiosis: It is a disease which irritates lungs. It causes scarring or fibrosis of
Similar Questions for you
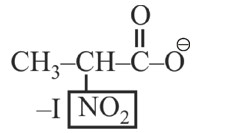
–I effect ∝ Acidic strength
+I effect ∝ Basic strength
* Most stable anion due to maximum –I effect.
* Most acidic
with increase in separation of screen from slits plane, fringe width increases.
Excessive nitrate in drinking water causes methemoglobinemia
Excessive nitrate in drinking water causes methemoglobinemia
Release of toxic/undesirable materials in the environment.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering