14.45. Define (a) eutrophication (b) pneumoconiosis (c) Photochemical smog (d) Classical smog
14.45. Define (a) eutrophication (b) pneumoconiosis (c) Photochemical smog (d) Classical smog
-
1 Answer
-
(a) Eutrophication: When the growth of algae increases in the surface of water, dissolved oxygen in water is reduced. This phenomenon is known as eutrophication. (Due to this growth of fish gets inhibited).
(b) Pneumoconiosis: It is a disease which irritates lungs. It causes scarring or fibrosis of the lung.
(c) Photochemical smog: Photochemical smog is formed as a result of photochemical decomposition of nitrogen dioxide and chemical reactions involving hydrocarbons. It takes place during dry warm season in presence of sunlight. It is oxidising in nature.
(d) Classical smog: Classical smog is formed due to condensation of SO, vapours on particles of carbon in cold climate. It is generally formed during winter when there is severe cold.It is reducing in nature.
Similar Questions for you
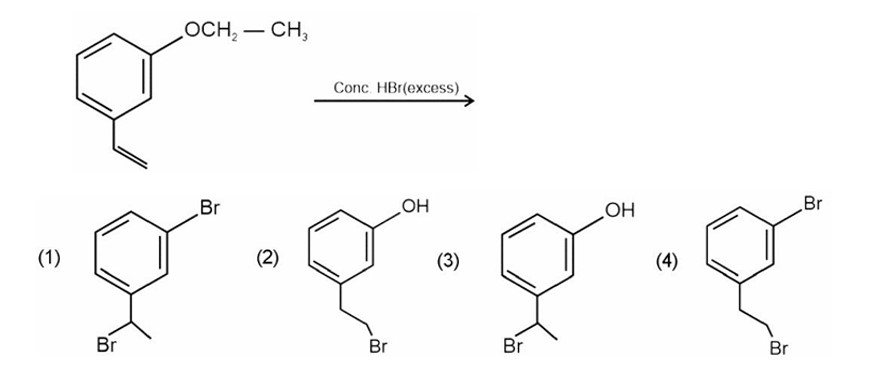
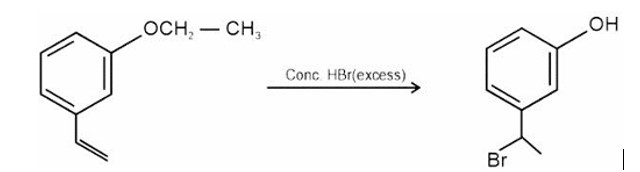
HBr adds to alkene in accordance with Markovnikov's rule.
Delocalisation of
To study Hydrocarbons for NEET, you can use the Hydrocarbons Class 11th NCERT solutions PDF.
Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatics hydrocarbons are the four main hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made of only carbon and hydrogen.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers