4.18. Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
4.18. Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
-
1 Answer
-
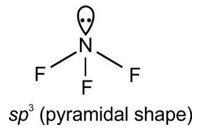
4.18. When two dissimilar atoms having different electronegativities combine to form a covalent bond, the bond pair of electrons is not shared equally. The bond pair shifts towards the nucleus of the atom having greater electronegativity. As a result, electron distribution gets distorted and the electron cloud is displaced towards the electronegative atom.
As a result, the electronegative atom becomes slightly negatively charged while the other atom becomes slightly positively charged. Thus, opposite poles are developed in the molecule and this type of a bond is called a polar covalent bond.
For example, in hydrogen fluoride molecule (HF
...more
Similar Questions for you
He2 has zero bond order hence it does not exist.
The three fundamental laws of chemistry are - Law of Definite Proportions, Law of Conservation of Mass, and Law of Multiple Proportions.
The three types of chemical bonds are - ionic, metallic and covalent bonds. When the electrons transfer between the atoms, they form the Ionic bonds by producing charged ions that are attracted to each other. When atoms share electrons, covalent bonds are created. When metal atoms share a sea of delocalized electrons, metallic bonds get created.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers