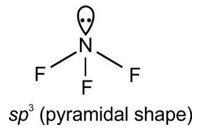
4.33. Explain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valence bond theory.
4.33. Explain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valence bond theory.
-
1 Answer
-
4.33. Let us consider the combination between atoms of hydrogen HA and HB and eA and eB be their respective electrons.
As they tend to come closer, two different forces operate between the nucleus and the electron of the other and vice versa. The nuclei of the atoms as well as their electrons repel each other. Energy is needed to overcome the force of repulsion. Although the number of new attractive and repulsive forces is the same, but the magnitude of the attractive forces is more. Thus, when two hydrogen atoms approach each other, the overall potential energy of the system decreases. Thus, a stable molecule of hydrogen is formed
...more
Similar Questions for you
He2 has zero bond order hence it does not exist.
The three fundamental laws of chemistry are - Law of Definite Proportions, Law of Conservation of Mass, and Law of Multiple Proportions.
The three types of chemical bonds are - ionic, metallic and covalent bonds. When the electrons transfer between the atoms, they form the Ionic bonds by producing charged ions that are attracted to each other. When atoms share electrons, covalent bonds are created. When metal atoms share a sea of delocalized electrons, metallic bonds get created.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers