42. The main reactions occurring in blast furnaces during extraction of iron from haematite are
(i) Fe2O3+3CO→2Fe+3CO2
(ii) FeO+SiO2→FeSiO3
(iii) Fe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CO
(iv) CaO+SiO2→CaSiO3
42. The main reactions occurring in blast furnaces during extraction of iron from haematite are
(i) Fe2O3+3CO→2Fe+3CO2
(ii) FeO+SiO2→FeSiO3
(iii) Fe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CO
(iv) CaO+SiO2→CaSiO3
-
1 Answer
-
42. Option (i) and (iv)
(i) Carbon monoxide is the primary reducing agent in the furnace.
(ii) This is an endothermic reaction in which heat is absorbed from the furnace. As a result, it is critical not to add too much limestone, as this will cool the furnace. Calcium oxide is a basic oxide that reacts with acidic oxides in the rock, such as silicon dioxide. Calcium silicate is formed when calcium oxide reacts with silicon dioxide.
Similar Questions for you
is the temperature Co-efficient of cell. The cell having less variation of EMF, with respect to temperature have high efficiency.
Below 1350° C, Mg can reduce Al2O3 and above 1350°C, Al can reduce MgO (from Ellingham diagram).
Melting and boiling point of Mg are lower than that of Al.
In ores/mineral available earthy and undesired impurities are gangue
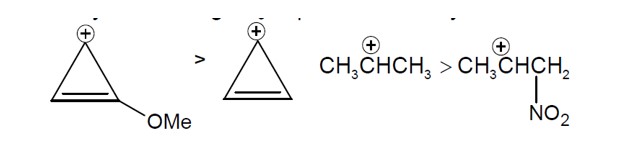
Sol. Reactivity towards depend on stability of carbocation formed
Leaching involves the given reaction,
Here, O2 is required for formation of Au (l) cyanide complex but no complex in absence of O2.
In above displacement reaction, Zn is oxidized.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers