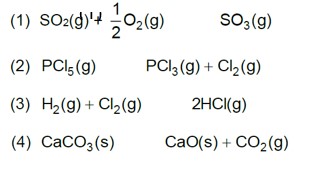
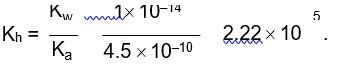7.22. Bromine monochloride (BrCl) decomposes into bromine and chlorine and reaches the equilibrium:
2BrCl (g) ⇌ Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
The value of Kc is 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3.3 x10-3mol L-1, what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
7.22. Bromine monochloride (BrCl) decomposes into bromine and chlorine and reaches the equilibrium:
2BrCl (g) ⇌ Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
The value of Kc is 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3.3 x10-3mol L-1, what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
Let x moles of BrCl decompose in order to attain the equilibrium. The initial molar concentration and the molar concentration at equilibrium point of different species may be represented as follows:
2BrCl2?(g) ?→?Ar2?(g)+Cl2?(g)
3.3*10−3m 0 0
3.3*10−3−2αα? α
∴ Kc?= (α*α)
Similar Questions for you
0.01 M NaOH,
M = 1 * 10-2
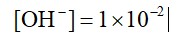
pOH = 2
pH = 2
Kp = Kc (RT)Dng
36 * 10–2 = Kc (0.0821 * 300)–1
Kc = 0.36 * 0.0821 * 300 = 8.86 » 9
A(g) ->B(g) + (g)
Initial moles n 0 &nbs
On increasing pressure, equilibrium moves in that direction where number of gaseous moles decreases.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th 2023
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering