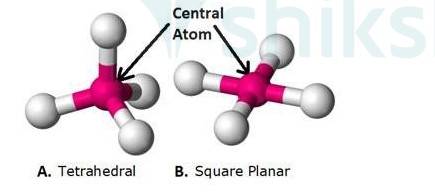
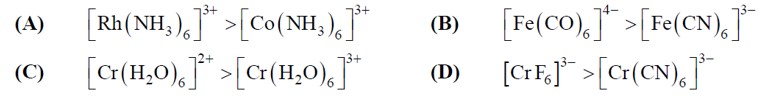9.13 Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ligand, coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
9.13 Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ligand, coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
-
1 Answer
-
(1) Coordination Entity: Coordination entity is a charged entity having positive or negative charge in which the central atom is surrounded by molecules which may be neutral/negatively charged called Ligands
Examples:
i. Cationic Complexes: [Cu (H2O)6]2+, [Al (H2O)6]3+
ii. Anionic Complexes: [CuCl4]2-, [Al (H2O)2 (OH)4]-
iii. Neutral Complexes: [Co (NH3)4 Cl2], [Ni (CO)4]
(2) Ligands: Ligands are the neutral or negatively charged entities surrounding the central metal atom of the coordination complex which possesses at least one unshared pair of electrons
Example: F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, H20, and NH3
(3) Coordination Number: Coordina
...more
Similar Questions for you
CoCl3.NH3 + AgNO3
x = 5
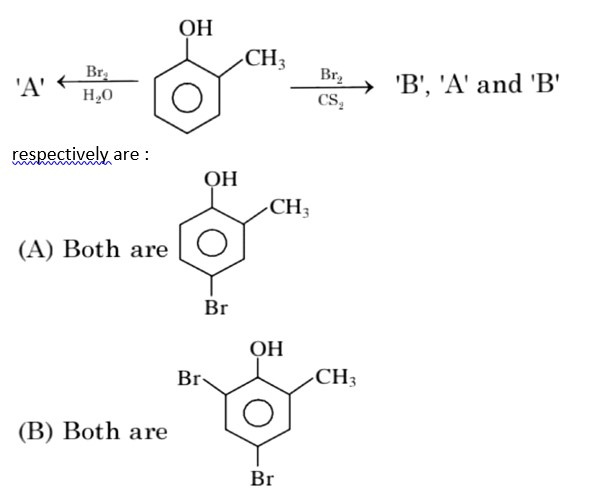
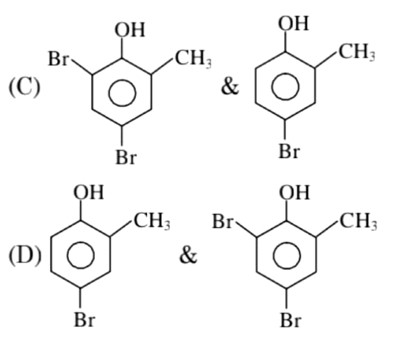
In H2O (polar solvent) dibromophenol derivative and in CS2 (non-polar solvent moneobromo phenol derivate is obtained.
3d => 4d => 5d CFSE increases for the same ligands.
Factual
⇒ leaching methods is used for those metal in which metal is more soluble than impurities and these are Al, Au, Ag, low grade Cu
σ bonded organometallic compound ⇒ M – C
σ-bond
and in π – bonded organo metallic compound
M – C
π bond
In ferrocene, there is π-bond
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers