9.19 How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? (i) [Cr(C2O4)3] 3– (ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
9.19 How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? (i) [Cr(C2O4)3] 3– (ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
-
1 Answer
-
(i) No geometrical isomer is possible for [Cr (C2O4)3]3– because the ligand C2O 2- is bidentate ligand (which have two sites of attachment to the central atom) and also in the coordination sphere it is the only ligand bond to it.
(ii) In the coordination sphere of [Co (NH3)3Cl3] there are two types of ligands present i.e NH3 and Cl- . Coordination number is There are 2 isomers possible for the complex:
Facial: In this isomer one type of ligand say NH3 forms the face of the square bipyramidal (triangular) structure.
Meridional: In this isomer one type of ligand are along the central axis of the pyramidal structure.
Similar Questions for you
CoCl3.NH3 + AgNO3
x = 5
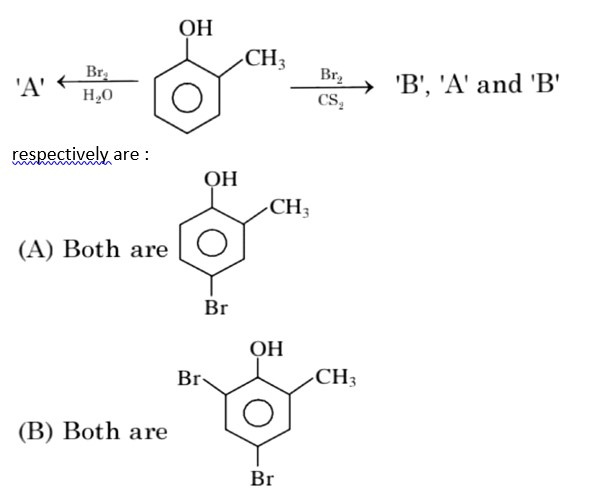
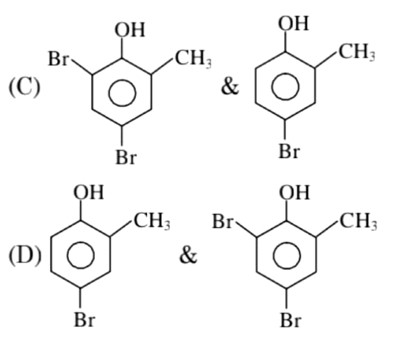
In H2O (polar solvent) dibromophenol derivative and in CS2 (non-polar solvent moneobromo phenol derivate is obtained.
3d => 4d => 5d CFSE increases for the same ligands.
Factual
⇒ leaching methods is used for those metal in which metal is more soluble than impurities and these are Al, Au, Ag, low grade Cu
σ bonded organometallic compound ⇒ M – C
σ-bond
and in π – bonded organo metallic compound
M – C
π bond
In ferrocene, there is π-bond
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers