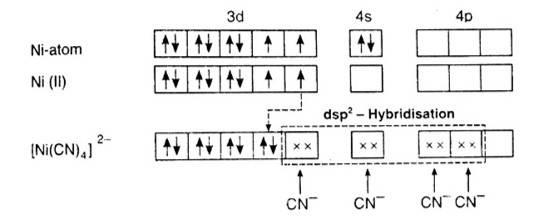
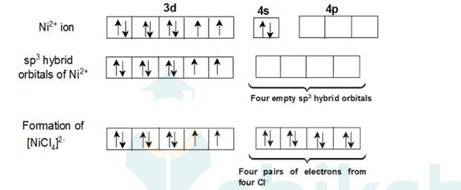
9.5 Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4 ] 2– ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4 ] 2– ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
9.5 Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4 ] 2– ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4 ] 2– ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
-
1 Answer
-
According to the valence band theory, the central metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n-1)d, ns, np (inner orbital complex) or ns, np, and (outer orbital complex)orbitals for hybridisation to form equivalent set of orbitals of definite geometry.
In [Ni (CN)4]2-, oxidation state of Ni can be calculated as :
Using overall charge balance as the whole ion has overall -2 charge:
x + 4 (-1) = -2 (? CN- has -1 negative charge) x = + 2
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Ni is: [Ar]3d84s2 Where, [Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 = [Ar]3d8 Outer electronic configuration of Ni+2 = 3
...more
Similar Questions for you
CoCl3.NH3 + AgNO3
x = 5
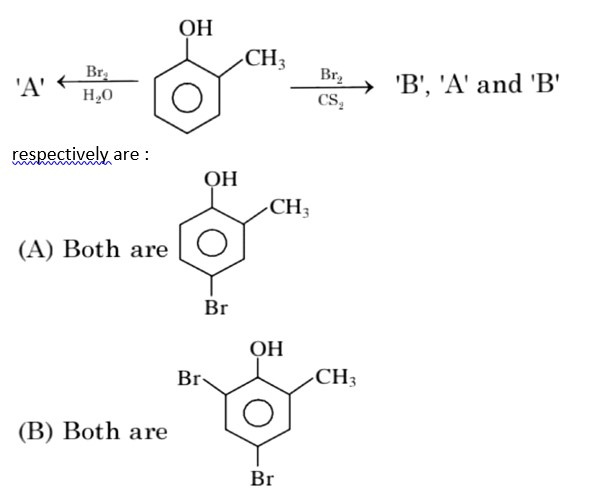
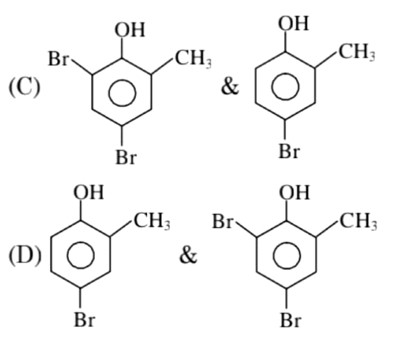
In H2O (polar solvent) dibromophenol derivative and in CS2 (non-polar solvent moneobromo phenol derivate is obtained.
3d => 4d => 5d CFSE increases for the same ligands.
Factual
⇒ leaching methods is used for those metal in which metal is more soluble than impurities and these are Al, Au, Ag, low grade Cu
σ bonded organometallic compound ⇒ M – C
σ-bond
and in π – bonded organo metallic compound
M – C
π bond
In ferrocene, there is π-bond
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers