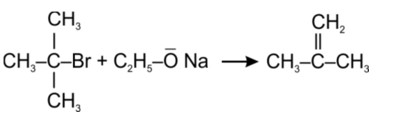
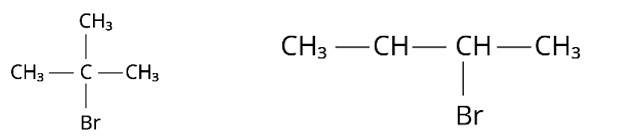Compound 'A' with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound 'A' only. When another optically active isomer 'B' of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and KOH both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ' A' and ' B '.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
Compound 'A' with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound 'A' only. When another optically active isomer 'B' of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and KOH both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ' A' and ' B '.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
-
1 Answer
-
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Because the rate of reaction of compound ‘A' with aqueous KOH is solely dependent on the concentration of ‘A, ' the reaction mechanism is SN1and ‘A' is 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane (tertiary bromide).
‘B', on the other hand, is an isomer of ‘A' and is optically active. As a result, ‘B' has to be 2-Bromobutane. Because the rate of reaction of ‘B' with aqueous KOH is determined by its concentration, the reaction mechanism is SN2.
(ii) Compound ‘B' will have an inverted conformation as a result of the SN2 reaction,
...more
Similar Questions for you
Photodiode in reverse bias mode is used as intensity measuring device.
Tertiary haloalkane does not undergo SN2 reaction
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers