Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
A[g] + 2B[g]→2C
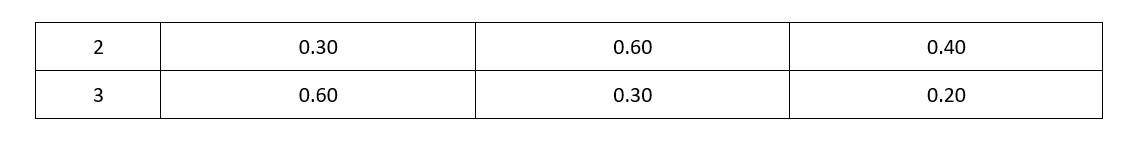
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.

A. Rate = k[A] 2[B]
B. Rate = k[A][B]2
C. Rate = k[A][B]
D. Rate = k[A]2[B]0
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
A[g] + 2B[g]→2C
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.


-
1 Answer
-
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option B
Let order of A and B be x and y.
r = k [A]x [B]y
0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.3)y_______1
0.4 = 0.1 = k (0.3)x (0.6)y_______2
0.2 = 0.1 = k (0.6)x (0.3)y______3
Divide 2 by 1
=
Divide 3 by 1
=
Hence Rate law is
r = k [A]1 [B]2
Similar Questions for you
Kindly go through the solution
Ea = 216.164kJ/mol 216
Reaction rate is used to measure how fast or slow reactions occur per unit time. The rate constant is a proportionality factor that remains constant for every reaction.
Yes, in elementary reactions, order and molecularity can be the same, but this is not always the case because order is an experimental quantity, and molecularity is a theoretical concept.
Reaction Kinetics, also known as chemical kinetics, is the study of the rate of chemical reaction and the factors affecting the reaction rate, such as temperature, concentration, and catalyst.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
