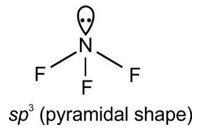
Comprehension given below is followed by some multiple choice questions. Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option.
Molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Two atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals called bonding molecular orbital (BMO) and anti bonding molecular orbital (ABMO). Energy of anti bonding orbital is raised above the parent atomic orbitals that have combined and the energy of the bonding orbital is lowered than the parent atomic orbitals. Energies of various molecular orbitals for elements hydrogen to nitrogen increase in the order :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< [ π2px = π2py] < σ2pz< [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
for oxygen and fluorine order of energy of molecular orbitals is given below :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< σ2pz< [ π2px = π2py] < [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
Different atomic orbitals of one atom combine with those atomic orbitals of the second atom which have comparable energies and proper orientation. Further, if the overlapping is head on, the molecular orbital is called 'Sigma', (σ) and if the overlap is lateral, the molecular orbital is called 'pi', (π). The molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the same rules as followed for filling of atomic orbitals. However, the order for filling is not the same for all molecules or their ions. Bond order is one of the most important parameters to compare the strength of bonds.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) In the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atoms 10 molecular orbitals will be formed.
(ii) All the molecular orbitals in the dioxygen will be completely filled.
(iii) Total number of bonding molecular orbitals will not be same as total number of anti bonding orbitals in dioxygen. (iv) Number of filled bonding orbitals will be same as number of filled anti bonding orbitals.
Comprehension given below is followed by some multiple choice questions. Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option.
Molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Two atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals called bonding molecular orbital (BMO) and anti bonding molecular orbital (ABMO). Energy of anti bonding orbital is raised above the parent atomic orbitals that have combined and the energy of the bonding orbital is lowered than the parent atomic orbitals. Energies of various molecular orbitals for elements hydrogen to nitrogen increase in the order :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< [ π2px = π2py] < σ2pz< [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
for oxygen and fluorine order of energy of molecular orbitals is given below :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< σ2pz< [ π2px = π2py] < [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
Different atomic orbitals of one atom combine with those atomic orbitals of the second atom which have comparable energies and proper orientation. Further, if the overlapping is head on, the molecular orbital is called 'Sigma', (σ) and if the overlap is lateral, the molecular orbital is called 'pi', (π). The molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the same rules as followed for filling of atomic orbitals. However, the order for filling is not the same for all molecules or their ions. Bond order is one of the most important parameters to compare the strength of bonds.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) In the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atoms 10 molecular orbitals will be formed.
(ii) All the molecular orbitals in the dioxygen will be completely filled.
(iii) Total number of bonding molecular orbitals will not be same as total number of anti bonding orbitals in dioxygen. (iv) Number of filled bonding orbitals will be same as number of filled anti bonding orbitals.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) The electronic configuration of dioxygen is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
(ii) As it can be seen from the electronic configuration of oxygen atom π*2p1X π*2p1Y the are partially. So, the statement g
Similar Questions for you
He2 has zero bond order hence it does not exist.
The three fundamental laws of chemistry are - Law of Definite Proportions, Law of Conservation of Mass, and Law of Multiple Proportions.
The three types of chemical bonds are - ionic, metallic and covalent bonds. When the electrons transfer between the atoms, they form the Ionic bonds by producing charged ions that are attracted to each other. When atoms share electrons, covalent bonds are created. When metal atoms share a sea of del
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering