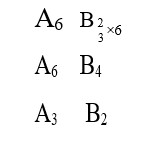Enthalpy is an extensive property. In general, if enthalpy of an overall reaction A→B along one route is ∆r H and ∆r H1, ∆rH2, ∆rH3 ..... represent enthalpies of intermediate reactions leading to product B. What will be the relation between ∆r H for overall reaction and ∆rH1 , ∆rH2 ..... etc. for intermediate reactions.
Enthalpy is an extensive property. In general, if enthalpy of an overall reaction A→B along one route is ∆r H and ∆r H1, ∆rH2, ∆rH3 ..... represent enthalpies of intermediate reactions leading to product B. What will be the relation between ∆r H for overall reaction and ∆rH1 , ∆rH2 ..... etc. for intermediate reactions.
-
1 Answer
-
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to Hess’s law, ΔrH = ΔrH1+ ΔrH2+ΔrH3
This is so because during the reaction A→ B, B’s formation undergoes various intermediate reactions, with the overall value of the enthalpy being ΔrH.
Similar Questions for you
Kindly go through the solution
(1) [Ni (NH3)6]+2 → Ni+2 → d8, C. No. = 6,
SP3d2, Para
(2) [Co (H2O)6]+2 → Co+2 → d6, C. No. = 6
d2sp3, Dia
(3) [Ti (H2O)6]+3 → Ti+3 → d1, C. No. = 6
d2SP3, Para
(4) [Co (NH3)6]+3 → Co+3 → d5, C. No. = 6
d2sp3, Para
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers