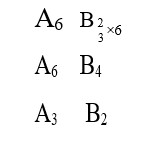For the reaction A(g) B(g) at 495 K, ΔrGo = -9.478kJ/mol. If we start the reaction in a closed container at 495 K with 22 millimoles of A, the amount of B in the equilibrium mixture is __________ millimoles
(Round off to the nearest Integer). [R=8.314 J/mol K; ln 10 = 2.303]
For the reaction A(g) B(g) at 495 K, ΔrGo = -9.478kJ/mol. If we start the reaction in a closed container at 495 K with 22 millimoles of A, the amount of B in the equilibrium mixture is __________ millimoles
(Round off to the nearest Integer). [R=8.314 J/mol K; ln 10 = 2.303]
ΔG° = -9.478 kJ/mol
Using ΔG° = -2.303 RT log K_p
-9.478 * 10³ = -2.303 * 8.314 * 495 log K_p
1 = log K_p ⇒ K_p = 10
Here, for the given reaction A (g)? B (g), K_p = K_c
Initial A = 22 mmol
At equilibrium A = 22 - x mmol; B = x mmol
K_c = [B] / [A] = (x/V) / (22-x)/V) = x / (22-x) = 10
x = 10 (22-x) ⇒ x = 2
Similar Questions for you
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
ΔH = –50.6 kJ/mol
NaOH + SA [HCl] → NaCl + H2O
ΔH = –55.9 kJ/mol
the value of ΔH for ionisation of CH3COOH
⇒ ΔH = +55.9 – 50.6
5.3 kJ/mol
Kindly consider the solution
Fact.
Kindly go through the solution
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering