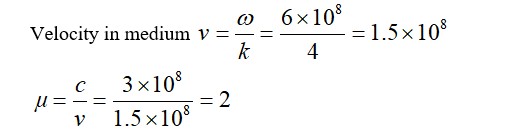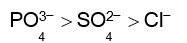Match the List-I with List-II
List – I List – II
(A) Lyophilic colloid (I) Liquid – liquid colloid
(B) Emulsion (II) Protective colloid
(C) Positively charged colloid (II) FeCl3 + NaOH
(D) Negatively charged colloid (IV) FeCl3 + hot water
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Match the List-I with List-II
List – I List – II
(A) Lyophilic colloid (I) Liquid – liquid colloid
(B) Emulsion (II) Protective colloid
(C) Positively charged colloid (II) FeCl3 + NaOH
(D) Negatively charged colloid (IV) FeCl3 + hot water
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Option 1 -
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III)
Option 2 -
(A)-(III), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(II)
Option 3 -
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(III), (D)-(IV)
Option 4 -
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV)
-
1 Answer
-
Correct Option - 1
Detailed Solution:Emulsion are liquid colloids, protective colloids are lyophilic, FeCl3 + H2O charged colloids and FeCl3 + NaOH (-ve)ly charged colloids.
Similar Questions for you
The process of settling of colloidal particles is
In physisorption multimolecular layers are formed on solid surface.
Emulsion is a colloidal solution of liquid in liquid.
Haemoglobin is a positive colloid. Hence greater is the charge of anion, more effective will be the coagulation of haemoglobin.
Therefore,
Correct order of coagulating power is
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers