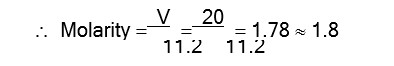Molecular hydrides are classified as electron deficient, electron precise and electron rich compounds. Explain each type with two examples.
Molecular hydrides are classified as electron deficient, electron precise and electron rich compounds. Explain each type with two examples.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Electron deficient hydrides are those that lack sufficient number of electrons to form typical covalent bonds. Group 13 hydrides, for example (BH3, AlH3, etc.).
(b) Electron precise: Electron precise hydrides are those that hav
Similar Questions for you
H2S has minimum boiling point.
PbS + 4H2O2->PbSO4 + 4H2O.
Volume strength of H2O2 = Molarity * 11.2
HF molecules are associated with strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding hence its boiling point is the highest
Compound Melting Point (K)
HF 190
HCl
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering