What is Kolbe's Electrolysis for symmetrical alkenes?
What is Kolbe's Electrolysis for symmetrical alkenes?
Kolbe's electrolysis is a process where an aqueous solution of sodium and potassium salt undergoes electrolysis to lead to the formation of a symmetrical alkene. Principle of this technique is that at anode, the carboxylate ion undergoes oxidation and loses carbon dioxide (CO? ). Similarly, at catho
Similar Questions for you
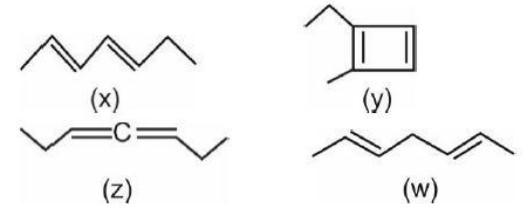
Stability order :
Conjugate > Isolated > Cumulative and (y) is Anti aromatic.
HOC ∝ 1 / (Stability of Alkene)
Kindly consider the following Image
According to this rule, when a hydrogen halide (HX) or water is added to an asymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen atom (H) gets attached to the carbon atom of the double bond which has more hydrogen atoms, and the halide (X) or OH group attaches to the carbon atom which has fewer hydrogen atoms.
The most common method used for the identification of alkenes is the bromine water test. We simply have to add a few drops of bromine water to the compound which is to be identified. If the compound actually is an alkene, the reddish brown colour will get decolorized (? bond reacts with bromine and
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Chemistry Hydrocarbon 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering