If the lines (x-k)/1 = (y-2)/2 = (z-3)/3 and (x+1)/3 = (y+2)/2 = (z+3)/1 are co-planar, then the value of k is…….
If the lines (x-k)/1 = (y-2)/2 = (z-3)/3 and (x+1)/3 = (y+2)/2 = (z+3)/1 are co-planar, then the value of k is…….
-
1 Answer
-
Determinant of vectors must be zero. Vector between points on lines: (-1-k, -2-2, -3-3). Vector directions: (1,2,3) and (3,2,1).
| -1-k, -4, -6; 1, 2, 3; 3, 2, 1 | = 0.
(-1-k) (2-6) - (-4) (1-9) + (-6) (2-6) = 0.
4 (1+k) - 32 + 24 = 0.
4+4k - 8 = 0. 4k=4 ⇒ k=1.
Similar Questions for you
....(1)
Let
Let
Put l1 and l2 in (1)
α = 3
Given , ,
Dot product with on both sides
... (1)
Dot product with on both sides
... (2)
(a – 1) × 2 + (b – 2) × 5 + (g – 3) × 1 = 0
2a + 5b + g – 15 = 0
Also, P lie on line
a + 1 = 2λ
b – 2 = 5λ
g – 4 = λ
2 (2λ – 1) + 5 (5λ + 2) + λ + 4 – 15 = 0
4λ + 25λ + λ – 2 + 10 + 4 – 15 = 0
30λ – 3 = 0
a + b + g = (2λ – 1) + (5λ + 2) + (λ + 4)
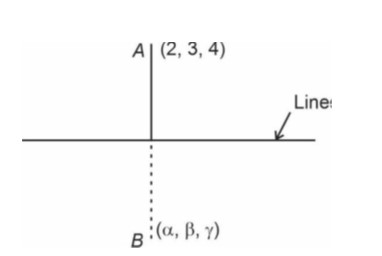
Take
x = 2λ + 1, y = 3λ + 2, z = 4λ + 3
= (α − 2)
Now,
(α − 2) ⋅ 2 + (β − 3) ⋅3 + (γ − 4) ⋅ 4 = 0
2α − 4 + 3β − 9 + 4γ −16 = 0
⇒ 2α + 3β + 4γ = 29
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
