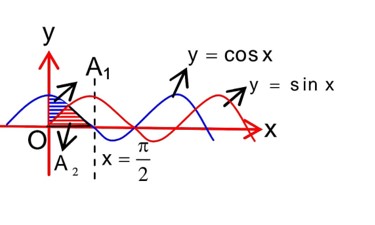
Let A1 be the area of the region bounded by the curves y = sinx, y = cosx and y-axis in the first quadrant. Also, let A2 be the area of the region bounded by the curves y = sinx, y = cosx, x-axis and x = in the first quadrant. Then,
Let A1 be the area of the region bounded by the curves y = sinx, y = cosx and y-axis in the first quadrant. Also, let A2 be the area of the region bounded by the curves y = sinx, y = cosx, x-axis and x = in the first quadrant. Then,
Option 1 - <p>A<sub>1</sub> = A<sub>2</sub> and A<sub>1</sub> + A<sub>2</sub> = <!-- [if gte mso 9]><xml>
<o:OLEObject Type="Embed" ProgID="Equation.DSMT4" ShapeID="_x0000_i1025"
DrawAspect="Content" ObjectID="_1819616356">
</o:OLEObject>
</xml><![endif]--> <span class="mathml" contenteditable="false"> <math> <mrow> <mroot> <mrow> <mn>2</mn> </mrow> <mrow></mrow> </mroot> </mrow> </math> </span></p>
Option 2 - <p>A<sub>1</sub> : A<sub>2</sub> = 1 : <!-- [if gte mso 9]><xml>
<o:OLEObject Type="Embed" ProgID="Equation.DSMT4" ShapeID="_x0000_i1025"
DrawAspect="Content" ObjectID="_1819616363">
</o:OLEObject>
</xml><![endif]--> <span class="mathml" contenteditable="false"> <math> <mrow> <mroot> <mrow> <mn>2</mn> </mrow> <mrow></mrow> </mroot> </mrow> </math> </span>and A<sub>1</sub> + A<sub>2</sub> = 1</p>
Option 3 - <p>A<sub>1</sub> : A<sub>2</sub> = 1 : 2 and A<sub>1</sub> + A<sub>2</sub> = 1</p>
Option 4 - <p>2A<sub>1</sub> = A<sub>2</sub> and A<sub>1</sub> + A<sub>2</sub> = 1 + <!-- [if gte mso 9]><xml>
<o:OLEObject Type="Embed" ProgID="Equation.DSMT4" ShapeID="_x0000_i1025"
DrawAspect="Content" ObjectID="_1819616378">
</o:OLEObject>
</xml><![endif]--> <span class="mathml" contenteditable="false"> <math> <mrow> <mroot> <mrow> <mn>2</mn> </mrow> <mrow></mrow> </mroot> </mrow> </math> </span></p>
8 Views|Posted 4 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
A
Answered by
4 months ago
Correct Option - 3
Detailed Solution:
Similar Questions for you
Required area = A
Note : No option in the question paper is correct.
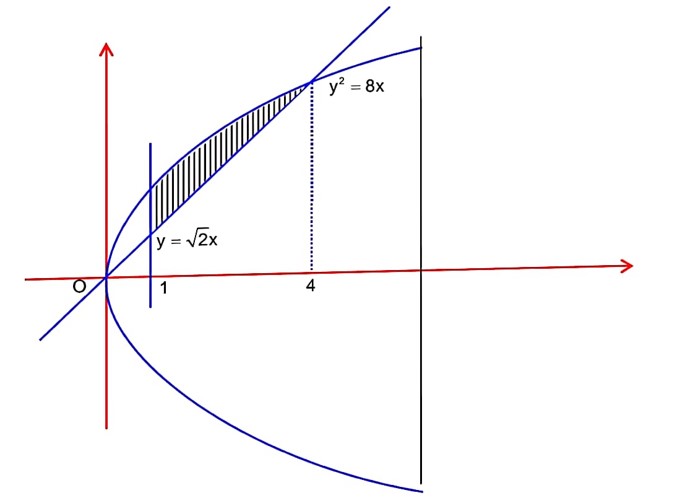
Required area = dx
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Maths Application of Integrals 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering