A circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis with angular speed ω₁. If another stationary disc having radius R/2 and same mass M is dropped co-axially on to the rotating disc. Gradually both discs attain constant angular speed ω₂. The energy lost in the process is p% of the initial energy. Value of p is
(Rotational)
A circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis with angular speed ω₁. If another stationary disc having radius R/2 and same mass M is dropped co-axially on to the rotating disc. Gradually both discs attain constant angular speed ω₂. The energy lost in the process is p% of the initial energy. Value of p is
(Rotational)
Angular momentum conservation:
⇒ I? ω? + I? ω? = (I? + I? )ωf
⇒ (MR²/2)ω? = (MR²/2 + MR²/8)ωf
⇒ ωf = 4/5 ω?
⇒ KEfinal = ½ (I? + I? )ωf² = (MR²ω? ²)/5
⇒ KEinitial = ½I? ω? ² = (MR²ω? ²)/4
⇒ % loss ⇒ 20%
Similar Questions for you
From A to B the process is isobaric
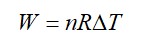
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering