(a) Pressure decreases as one ascends the atmosphere. If the density of air is ρ, what is the change in pressure dp over a differential height dh?
(b) Considering the pressure p to be proportional to the density, find the pressure p at a height h if the pressure on the surface of the earth is p0.
(c) If Po = 1.03*105 N m-2, ρo = 1.29 kg m-3 and g = 9.8 m s-2, at what height will the pressure drop to (1/10) the value at the surface of the earth?
(d) This model of the atmosphere works for relatively small distances. Identify the underlying assumption that limits the model.
(a) Pressure decreases as one ascends the atmosphere. If the density of air is ρ, what is the change in pressure dp over a differential height dh?
(b) Considering the pressure p to be proportional to the density, find the pressure p at a height h if the pressure on the surface of the earth is p0.
(c) If Po = 1.03*105 N m-2, ρo = 1.29 kg m-3 and g = 9.8 m s-2, at what height will the pressure drop to (1/10) the value at the surface of the earth?
(d) This model of the atmosphere works for relatively small distances. Identify the underlying assumption that limits the model.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) consider a horizontal parcel of air with cross section A and height dh
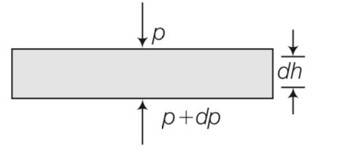
Let the pressure on the top surface and bottom surface be P and p+dp. If the parcel is in equilibrium , then the net upward force must be balanced by the weigh
Similar Questions for you
Surface tension is the force acting on the surface of the liquid.
Bernoulli's principle states that in a steady flow, the sum of pressure, kinetic energy per unit volume, and potential energy per unit volume remains constant.
Yes, the Mechanical properties of fluids class 11th physics is important in NEET. On average, 1-2 questions would be asked from this chapter, which you can cover from the Class 11th Mechanical Properties of Fluids notes.
The main mechanical properties of fluids are exerting pressure, resisting flow or viscosity, forming surface tension, following Bernoulli's principle, and moving in a streamline.
Since velocity does not change, so acceleration will be zero.
mg = FB + Fv
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Ten 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering
