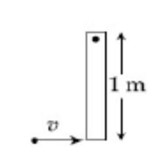
A thin rod of mass 0.9 kg and length 1 m is suspended, at rest, from one end so that in can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. A particle of move 0.1 kg moving in a straight line with velocity 80 m/s hits the rod at its bottom most point and sticks to it (see figure). The angular speed (in rad/s) of the rod immediately after the collision will be
A thin rod of mass 0.9 kg and length 1 m is suspended, at rest, from one end so that in can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. A particle of move 0.1 kg moving in a straight line with velocity 80 m/s hits the rod at its bottom most point and sticks to it (see figure). The angular speed (in rad/s) of the rod immediately after the collision will be
L_i = L_f
mvL = Iω
mvL = (ML³/3 + mL²)ω
Before collision
After collision
0.1 * 80 * 1 = (0.9 * 1²)/3 + 0.1 * 1²)ω
8 = (3/10 + 1/10)ω 8 = (4/10)ω ω = 20 rad/sec
Similar Questions for you
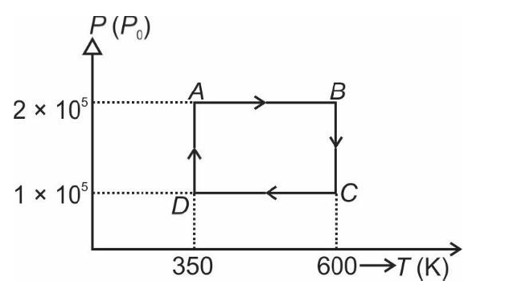
From A to B the process is isobaric
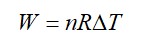
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering