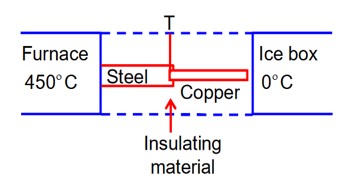
If K1 and K2 are the thermal conductivities, L1 and L2 are the lengths and A1 and A2 are the cross sectional areas of steel and copper rods respectively such that Then, for the arrangement as shown in the figure, the value of temperature T of the steel – copper junction in the steady state will be:
If K1 and K2 are the thermal conductivities, L1 and L2 are the lengths and A1 and A2 are the cross sectional areas of steel and copper rods respectively such that Then, for the arrangement as shown in the figure, the value of temperature T of the steel – copper junction in the steady state will be:
Option 1 - <p>18°C</p>
Option 2 - <p>14°C</p>
Option 3 - <p>45°C</p>
Option 4 - <p>150°C</p>
11 Views|Posted 6 months ago
Asked by Shiksha User
1 Answer
A
Answered by
6 months ago
Correct Option - 3
Detailed Solution:
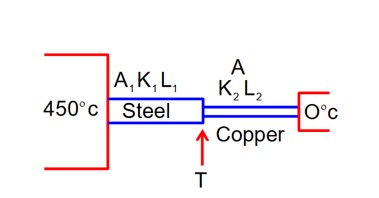
10 T = 450
T = 45° C
Similar Questions for you
Thermal stress is developed on heating when expansion of rod is hindered.
According to question, we can write
400 × 1 × 12.5 = 500 × 5 × (100 – 36.5)
S = 10 cal/mol °C
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
66K
Colleges
|
1.2K
Exams
|
6.9L
Reviews
|
1.8M
Answers
Learn more about...

Physics Thermal Properties of Matter 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
or
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
or
See what others like you are asking & answering