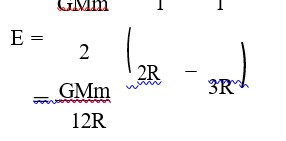On the x-axis and at a distance x from the origin, the gravitational field due to a mass distribution is given by Ax/(x²+a²)³/² in the x-direction. The magnitude of gravitational potential on the x-axis at a distance x, taking its value to be zero at infinity is:
On the x-axis and at a distance x from the origin, the gravitational field due to a mass distribution is given by Ax/(x²+a²)³/² in the x-direction. The magnitude of gravitational potential on the x-axis at a distance x, taking its value to be zero at infinity is:
Option 1 -
A(x² + a²)¹/²
Option 2 -
A/(x²+a²)³/²
Option 3 -
A(x² + a²)³/²
Option 4 -
A/(x²+a²)¹/²
-
1 Answer
-
Correct Option - 4
Detailed Solution:g = Ax / (x² + a²)³?²
⇒ ∫? dV = -∫?^∞ gdx
⇒ 0 - V = -∫?^∞ [Ax / (a² + x²)³?²] dx
Let, a² + x² = t²
⇒ 2xdx = 2tdt
⇒ xdx = tdt
⇒ V = ∫?^∞ (Atdt / t³) ⇒ [-A / t]?^∞ ⇒ [-A / √(a² + x²)]?^∞
⇒ V = A / √(a² + x²)
Similar Questions for you
Due to Interference, soap bubble appears coloured.
Value of 'g' increases at the equator when earth suddenly stops rotating.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers