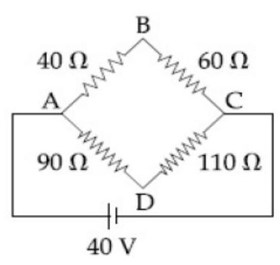
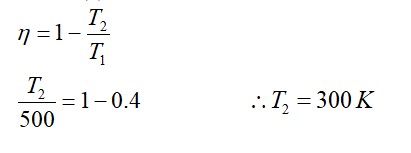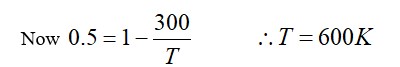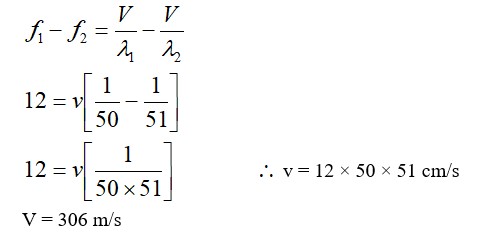The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure ΔP is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity ΔT at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were 300 K and 2 atm. respectively. If |ΔT| = C|ΔP| then value of C in (K/atm) is ….
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure ΔP is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity ΔT at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were 300 K and 2 atm. respectively. If |ΔT| = C|ΔP| then value of C in (K/atm) is ….
T = constant
P = constant
PV = nRT
PdV = nRdT
PdV + VdP = 0
ΔV = nRΔT/P
dV = (-)VdP/P
|ΔV| = V (ΔP/P)
V/P ΔP = nRΔT/P
ΔT = V/nR ΔP
C = V/nR T/P = 300/2 = 150
Similar Questions for you
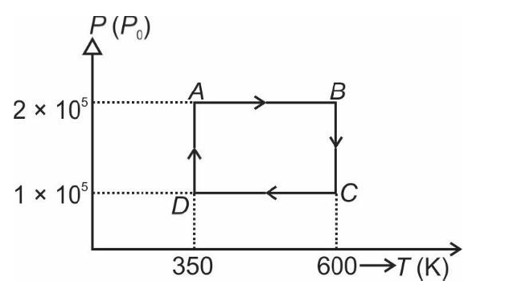
From A to B the process is isobaric
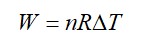
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Heat is path dependent so path function but internal energy does not depend on path chosen.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering