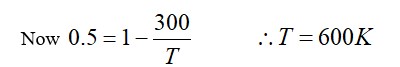The molar specific heat Cv of a diatomic gas is (5/2)R when we treat its molecules to be rigid having no vibrations. But this assumption is not always valid especially at high temperatures. In that case, molecules are treated as non-rigid having vibrational energy also. Cv for diatomic gas with non-rigid gas molecules will be:
The molar specific heat Cv of a diatomic gas is (5/2)R when we treat its molecules to be rigid having no vibrations. But this assumption is not always valid especially at high temperatures. In that case, molecules are treated as non-rigid having vibrational energy also. Cv for diatomic gas with non-rigid gas molecules will be:
Vibrational energy of a non-rigid gas molecule is K? T so, total energy = (5/2)K? T + K? T = (7/2)K? T
∴ C? = (7/2)R
Similar Questions for you
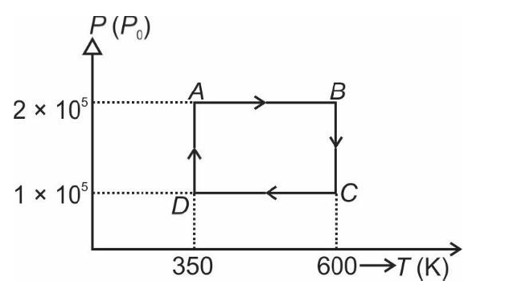
From A to B the process is isobaric
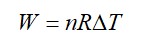
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Heat is path dependent so path function but internal energy does not depend on path chosen.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...
Didn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering