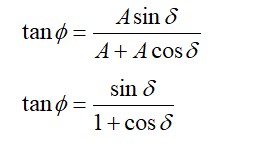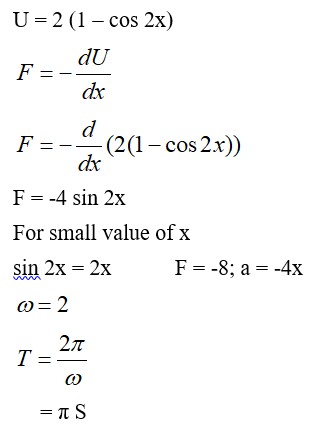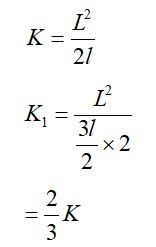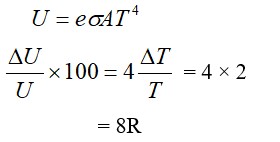Two identical cylindrical vessels are kept on the ground and each contain the same liquid of density d. The area of the base of both vessels is S but the height of liquid in one vessel is x1 and in the other, x2. When both cylinders are connected through a pipe of negligible volume very close to the bottom, the liquid flows from one vessel to the other until it comes to equilibrium at a new height. The change in energy of the system in the process is :
Two identical cylindrical vessels are kept on the ground and each contain the same liquid of density d. The area of the base of both vessels is S but the height of liquid in one vessel is x1 and in the other, x2. When both cylinders are connected through a pipe of negligible volume very close to the bottom, the liquid flows from one vessel to the other until it comes to equilibrium at a new height. The change in energy of the system in the process is :
sx? dg (x? /2) + sx? dg (x? /2)
Uf = (S (x? +x? )/2)gd (x? +x? )/4) x 2
= S (x? + x? )²gd/4
U? -Uf = (Sgd/4) {2x? ² + 2x? ² − (x? + x? )²}
= (Sgd/4) (x? -x? )²
Similar Questions for you
From A to B the process is isobaric
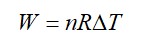
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering