When a long glass capillary tube of radius 0.015 cm is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises to a height of 15 cm within it. If the contact angle between the liquid and glass to close to 0°, the surface tension of the liquid, in milli Newton m?¹, is [ρ(liquid) = 900kgm?³, g = 10 ms?²] (Give answer in closest integer)
When a long glass capillary tube of radius 0.015 cm is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises to a height of 15 cm within it. If the contact angle between the liquid and glass to close to 0°, the surface tension of the liquid, in milli Newton m?¹, is [ρ(liquid) = 900kgm?³, g = 10 ms?²] (Give answer in closest integer)
The height of capillary rise is given by the formula:
h = (2T cosθ) / (rρg)
Given: h = 15 cm = 0.15 m, r = 0.015 cm = 1.5 * 10? m, ρ = 900 kg/m ³, g = 10 m/s², and θ ≈ 0° (so cosθ ≈ 1).
We need to find the surface tension, T.
T = (h r ρ g) / (2 cosθ)
T = (0.15 * 1.5 * 10? * 900 * 10) / 2
T = 0.10125 N/m
Th
Similar Questions for you
From A to B the process is isobaric
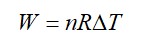
= W = 2 × R (600 - 350)
= 500 R
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else.
On Shiksha, get access to
Learn more about...

Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids 2025
View Exam DetailsMost viewed information
SummaryDidn't find the answer you were looking for?
Search from Shiksha's 1 lakh+ Topics
Ask Current Students, Alumni & our Experts
Have a question related to your career & education?
See what others like you are asking & answering